What makes Canadians Sick?
As the graph below illustrates, social factors are very influential; they can account for about half the variation in a person's health status.
These determinants affect all groups in Canada, both immigrant and non-immigrant. The factors commonly recognized as the social determinants that affect Canadians' lives are:

- Income
- Early childhood development
- Disability
- Education
- Social exclusion
- Social safety net
- Gender
- Employment/working conditions
- Race
- Aboriginal status
- Safe and nutritious food
- Housing/homelessness
- Community belonging
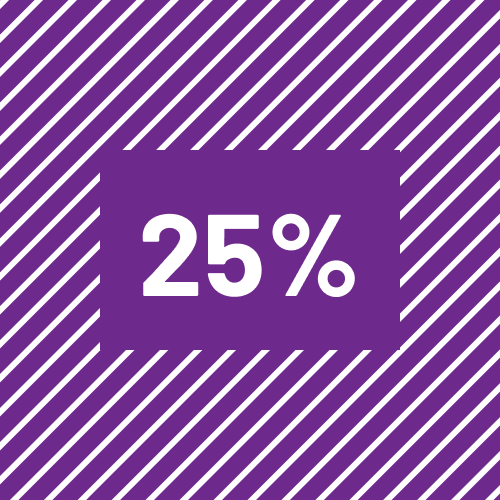
- Access to health care
- Health care system
- Wait times
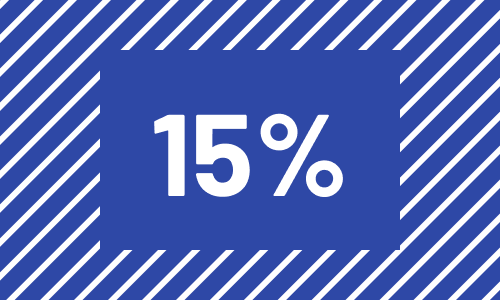
- Biology
- Genetics

- Air quality
- Civic infrastructure
The factors commonly recognized as the social determinants that affect Canadians' lives are:
-

Income and social status
-

Education and literacy
-
Employment and working conditions
-

Childhood experiences
-

Physical environments
-

Social supports and coping skills
-

Healthy behaviours
-

Access to health services
-

Biology and genetic endowment
-

Gender
-

Culture
-
Race/racism
Immigrant and refugees groups, however, are more likely than the Canadian-born population to be exposed to the social determinants that make them ill. Furthermore, compared to the Canadian-born population, immigrant and refugee groups more commonly experience specific factors such as those relating to pre- and post-migration, language difficulties and racism (Hansson et al., 2010; MHCC, 2016).
As an illustration of the ways in which social determinants experienced by immigrants and refugees may lead to differential impacts on their mental health, the following pages elaborate on the determinants of migration, followed by a discussion of income and socioeconomic status, employment and education, housing, and discrimination and racism post-migration. Although these five social determinants are not the only ones affecting immigrants and refugees, they are discussed here as their effects have been well-documented, and they serve to show the wide range of circumstances newcomers may experience within any of the determinants.